Helena could have fled Poland well before the Germans invaded her homeland in September 1939. As a wealthy Polish landowner in Debica, Helena Jablonowska quickly learned the Germans had targeted the elite as they ravaged the entire country. The Germans considered the aristocracy and the intelligentsia as most likely to lead any uprising against the Reich. Within six months, tens of thousands of Poland’s wealthiest and best-educated citizens were imprisoned and executed. How easy it would have been for Helena to pack her valuables and spend the war years in a neutral country! She instead chose to remain in her beloved homeland. As Helena stood and fought against German facism and Russian totalitarianism, she lost her family’s property, wealth, and status but never her compassion or integrity.

Helena Jablonowska was one of the most extraordinary women to rise up against the Germans during the Second World War. She was born on January 4, 1895, in Andrychow, Poland, and was, as one might say, “born to the service of others.” As the eldest daughter of Mikołaj Rey, a political activist associated with the peasant movement, Helena would follow in her father’s footsteps.
From 1906-1913, Jablonowska received an excellent education at a school for girls at the Convent of the Niepokalanki sisters in Jaroslaw. The sisters instilled a strong sense of moral duty for those in need and were themselves well-known rescuers of Jews and partisans during the wars.

The Convent in Jaroslaw
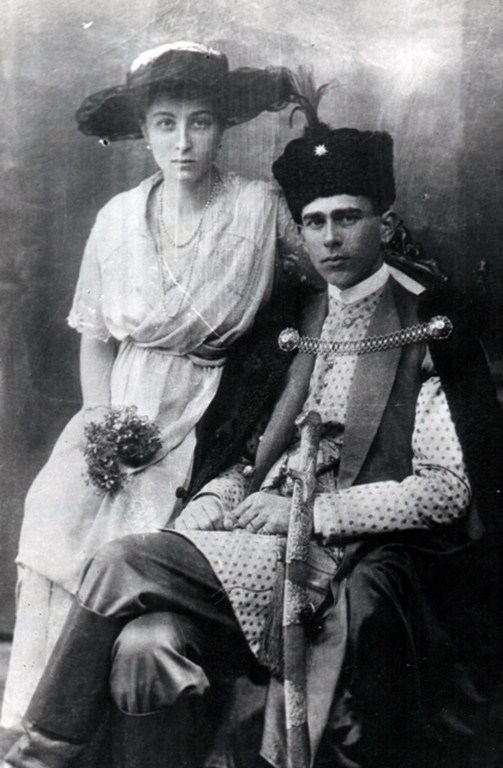

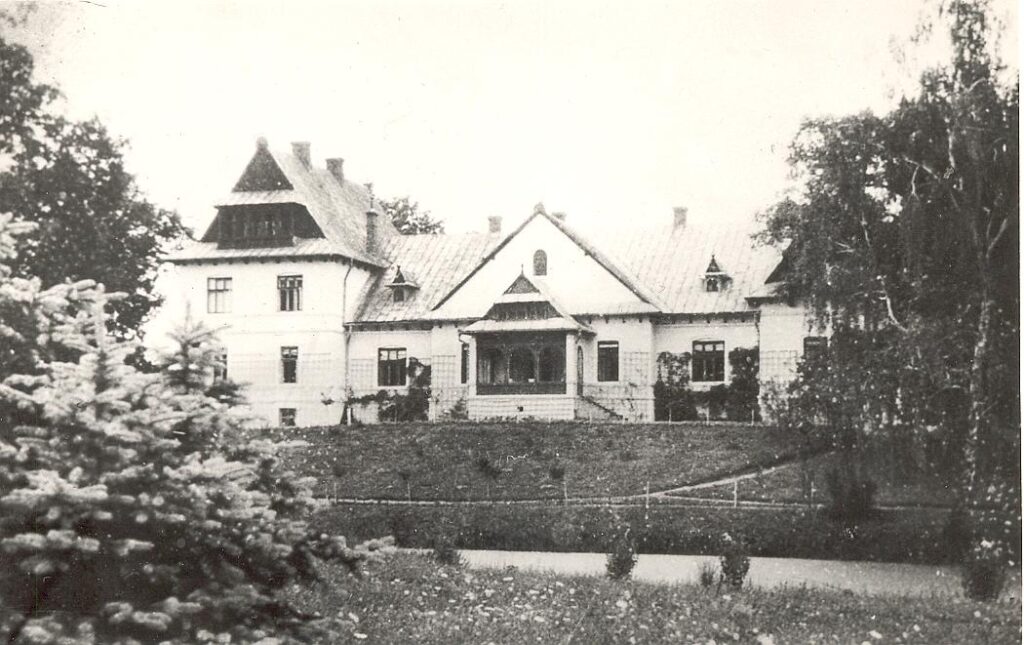
Helena married Jozef Jablonowski, a man whose family shared her zeal for political activism. After their marriage at the church her father funded in Chotowa, the young couple settled in the family’s manor in Przyborów, near Debica. Three sons and one daughter soon followed. As Helena raised her family during the interwar period, she was the president of the Catholic Action and Marian Sodality. She initiated efforts to organize orphanages where children from rural areas safely received care and food while their mother participated in agricultural work.

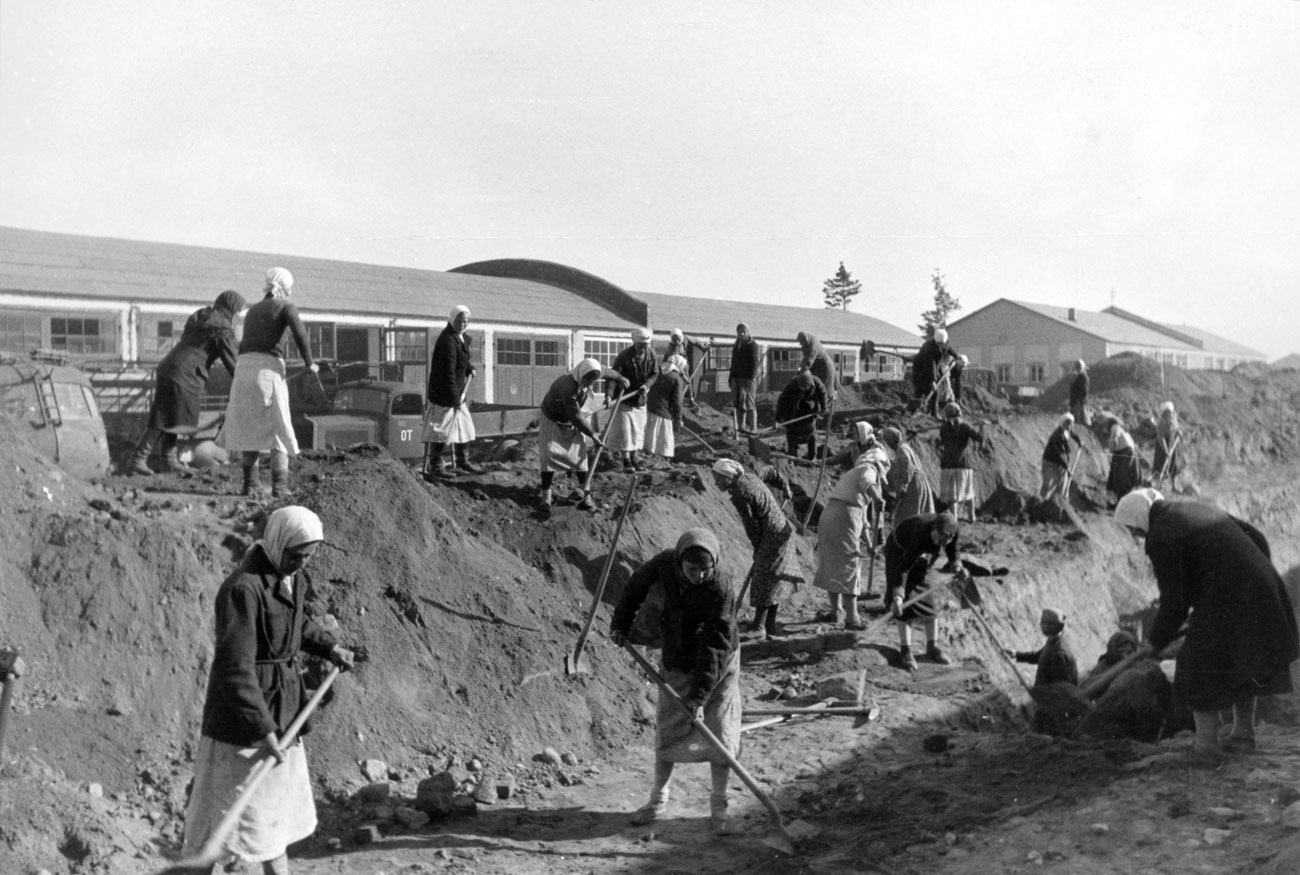
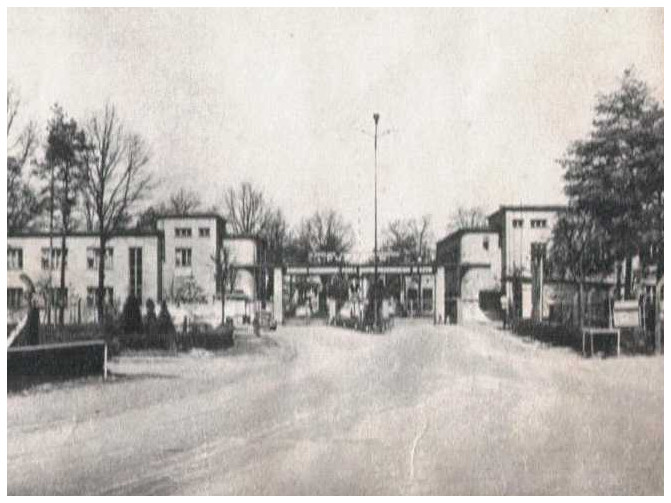
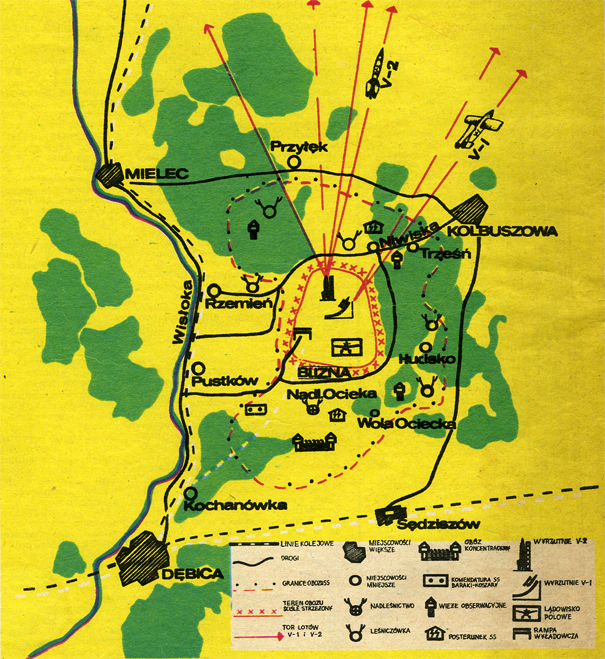
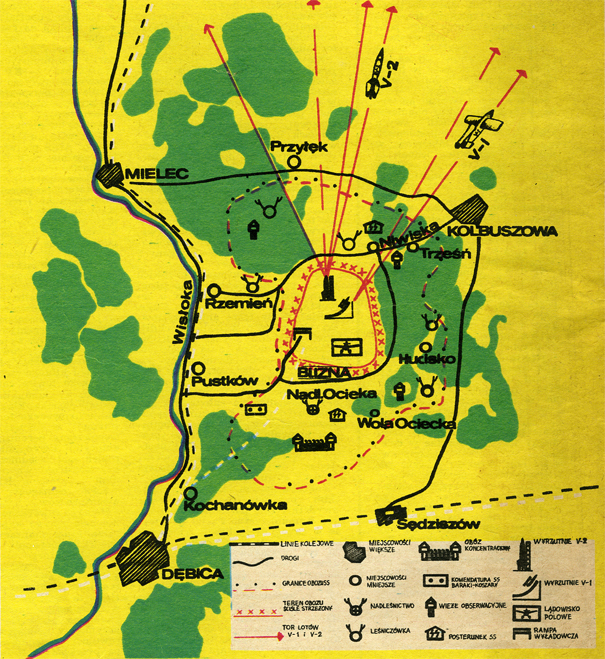
Helena’s greatest trials came with Germany’s invasion of Poland in 1939. The wilderness areas of Debica and the surrounding villages proved to be the perfect place for Hitler to build the largest SS training camp outside of Germany. Within the first few months of occupation, the Germans turned many of the local population into refugees as their homes were raised for building the camp. Those who chose to stay worked as forced laborers, felling trees and building the massive camp reaching from Debica to Kolbuszowa.
Helena’s love of Poland and her sacrificial nature were challenged by the atrocities all around her. Recognizing her family’s status and wealth, she exerted influence on behalf of those less fortunate. At significant risk to her family, the Jablonowski home became a shelter for the families of Polish soldiers and Polish Army officers, and displaced villagers.
Helena’s work with the Polish Home Army (AK) is perhaps her most remarkable achievement where she was known by the AK codename, “Rzepechia.” The Jablonowski home became a center of partisan activity, and her sons also were Home Army soldiers. One son, Andrzej, was shot by Germans while carrying a wounded partisan on his back during Operation Tempest.

As Camp Heidelager was expanded, separate prisons for Poles, Jews, and captured Russian soldiers were built in nearby Pustkow. Helena boldly requested a meeting with the camp commander, asking to help feed the starving prisoners. As her German was fluent, she was able to employ sizeable influence. To everyone’s surprise, the commandant allowed Helena and her daughter Marysia to organize a weekly food collection for the prisoners. Helena also acted as an intermediary in collecting letters and secret messages from prisoners to their families and the outside world. She even assisted in the escape of some prisoners at Pustkow.
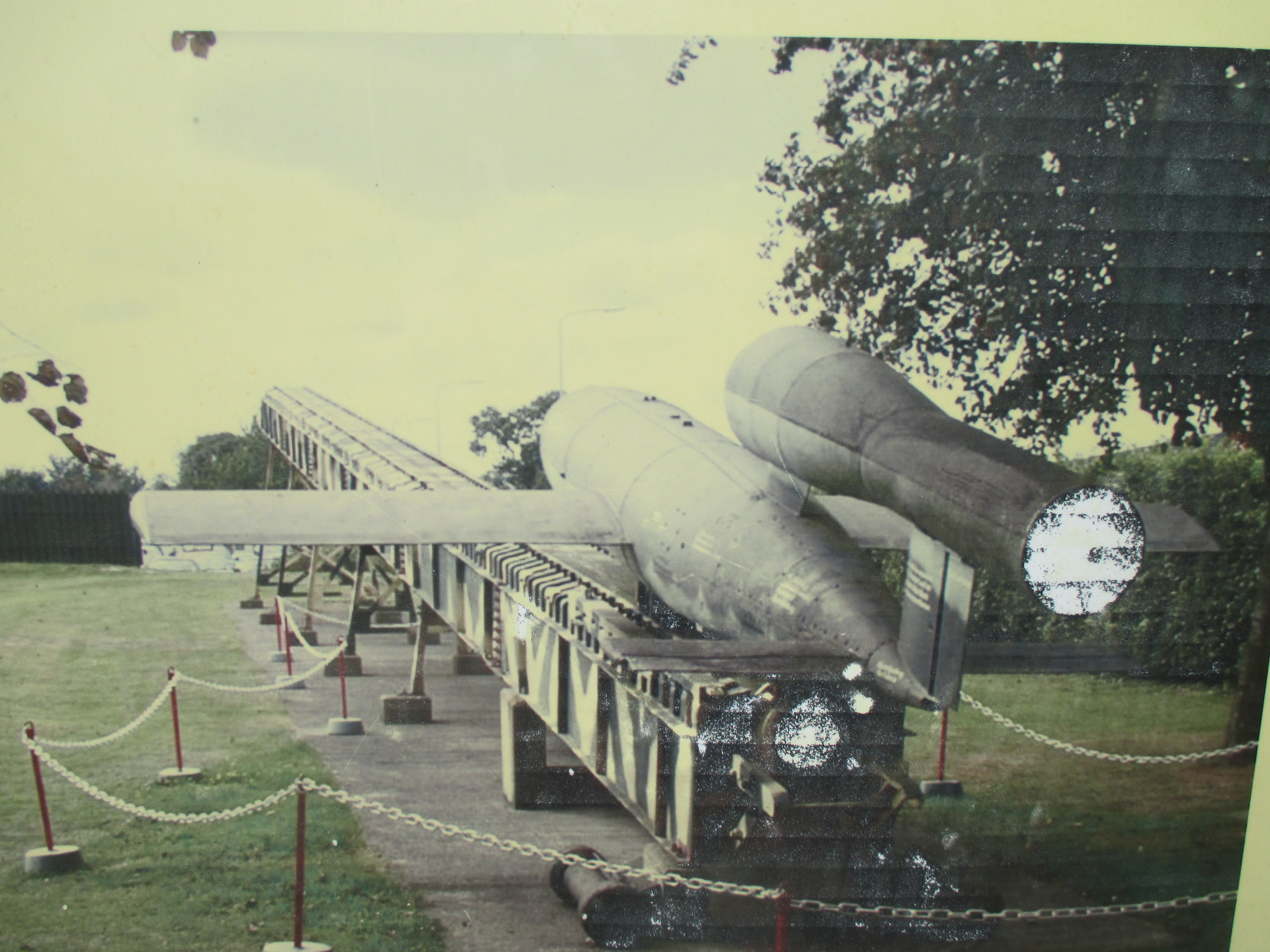
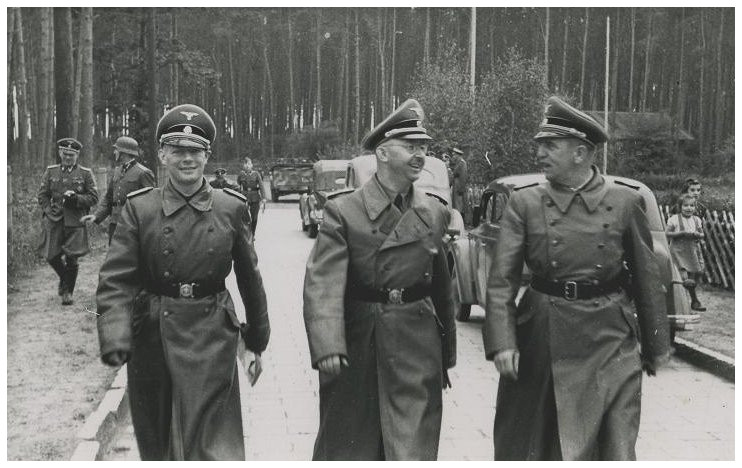
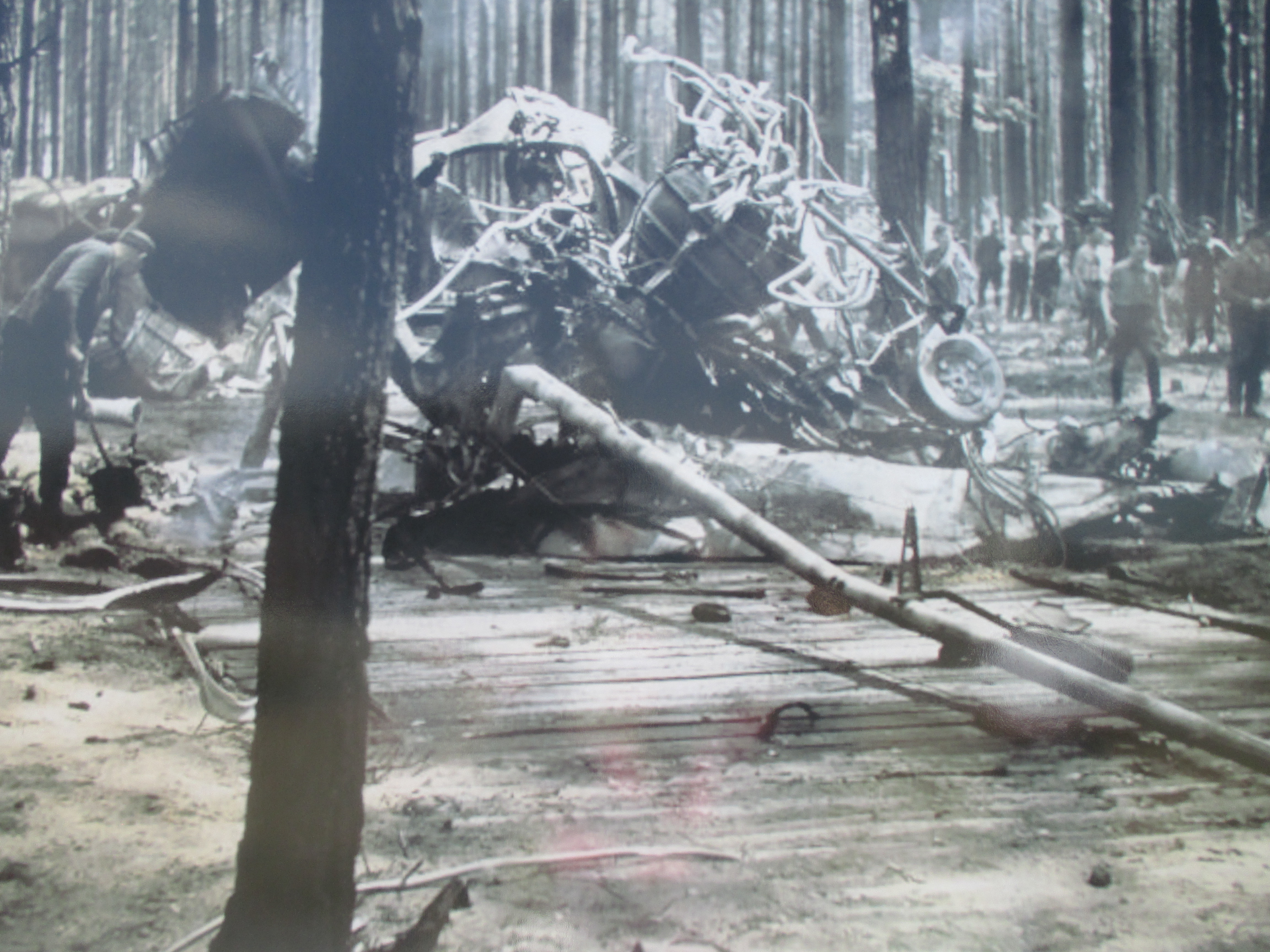
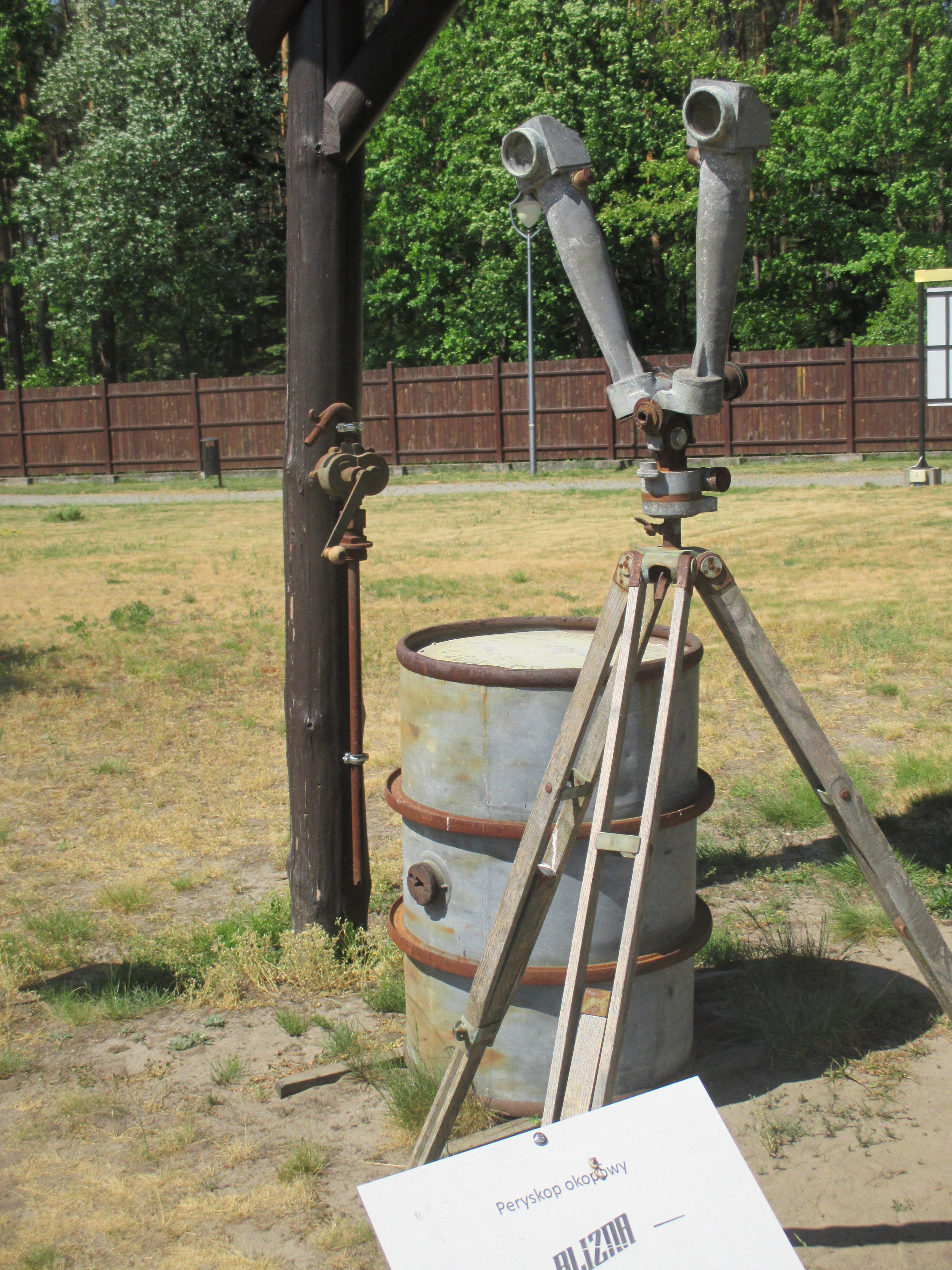
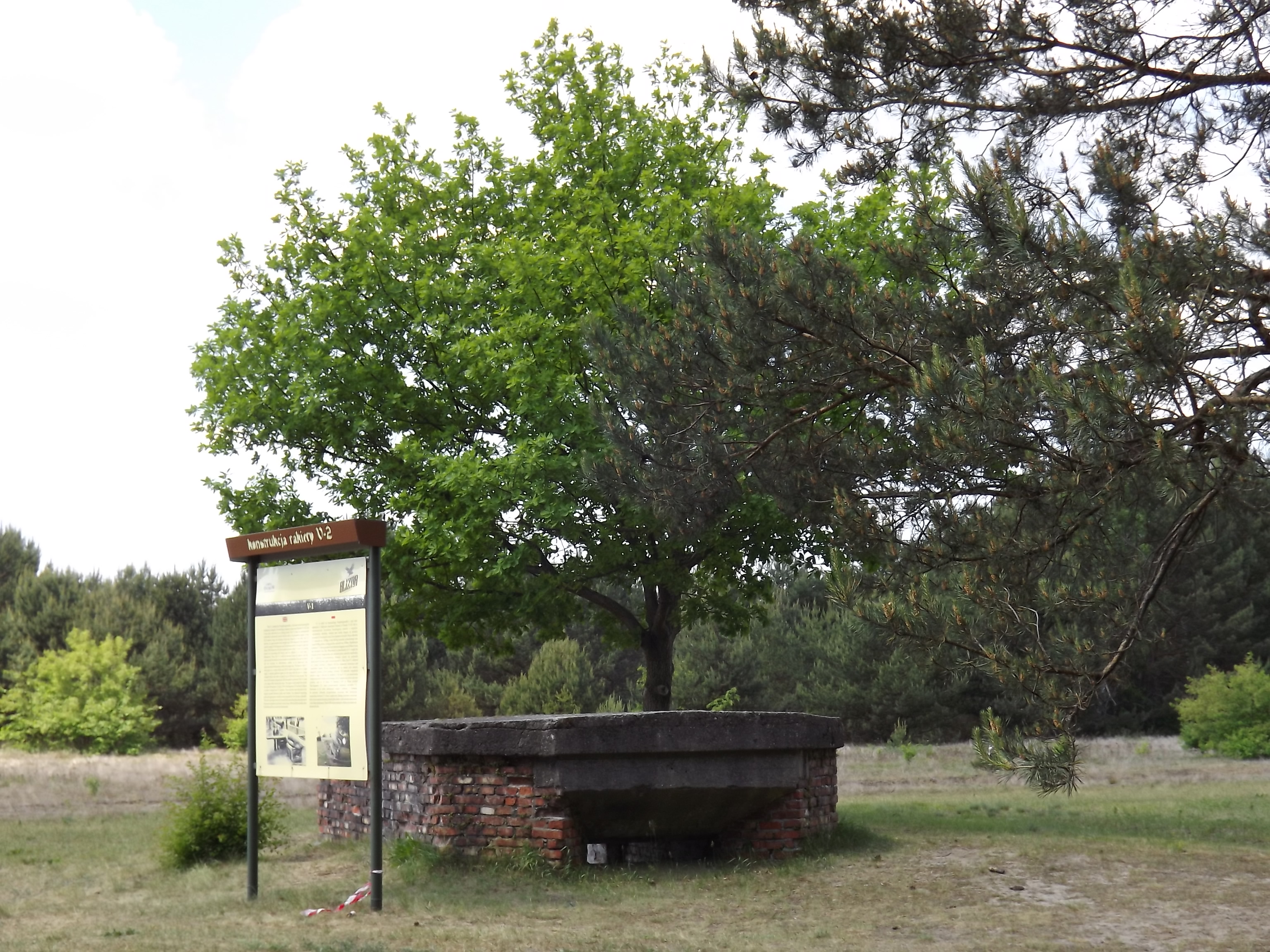
Through her various activities at the camp, Helena gathered information about the number and condition of the prisoners and Pustkow Prison Camp’s functioning. She also collected information about Hitler’s top-secret V-1 and V-2 missile research in nearby Blizna, inside Camp Heidelager. Helena passed the details on to the command of the Polish Home Army.

Eventually, Debica became too dangerous for the AK officials, so they move their headquarters (known as Deser) to Gumniska, a hilly area south of town. Resistance fighters engaged in acts of sabotage and often attacked the trains carrying German troops on the Krakow-Lwow rail lines.
In early 1944, the AK attempted to blow up a train carrying Hans Frank as it passed through a station near Debica. The Germans arrested innocent villagers from nearby Gumniska to send to prison camps as retribution, known as “collective punishment.” While the prisoners waited in German trucks in front of an administrative building, Helena Jablonowska opened the building gate and truck doors holding the prisoners. Taking advantage of the confusion, the prisoners scattered around the city. The Germans managed to catch only eleven people and were furious. Helena was dismissed from her position as chairman of the Central Welfare Council of Debica, but the decision was never enforced.
As the Russian “rescuers” moved into the area in July 1944, the locals fled from the towns and villages to avoid the ensuing battles. Together with three hundred locals, the Duchess remained in hiding for several weeks in cellars and outbuildings. The Germans destroyed the Jablonowski manor house and farm buildings as they fled from the Russians in the late summer of 1944.
The new communist government that occupied Poland from 1944-1989 extended no mercy to the Countess. As was typical of the Russians, they burned complete libraries at manor homes and any item that might work against their totalitatian ideology. Helena was stripped of all her property by the puppet government even though the community attested to her good works during the German occupation. Helena moved to Krakow and never complained about her unfair treatment or sacrifice. This amazing woman understood the importance of living in contentment despite her circumstances.
On June 11, 1977, Helena died at the age of eighty-three and was buried in the family chapel in Straszecin. Her husband, Jozef, died in Krakow in 1966.

In 2007, the European Union announced it would completely rebuild the Jablonowski’s manor in Przyborów. Helena’s father, Mikołaj Rey, a member of Parliament and descendant of the “Father of Polish literature” built the manor house in 1894. Its architect was Stanislaw Witkiewicz, founder of the “Zakopane Style.” It is the only existing manor house of this type that remains. Currently, the manor house remains in ruins.
Helena’s story is a testimony is an inspiration to those of us who might despair in the current world around us. She acted boldly, not for her own interests, but for the welfare of others.